使用LSTM建立seq2seq模型进行语言翻译
生活随笔
收集整理的這篇文章主要介紹了
使用LSTM建立seq2seq模型进行语言翻译
小編覺得挺不錯的,現在分享給大家,幫大家做個參考.
文章目錄
- 1. 數據處理
- 2. 編碼器、解碼器數據
- 2.1 編碼器
- 2.2 解碼器
- 2.3 模型
- 3. 訓練
- 4. 推理模型
- 5. 采樣
參考 基于深度學習的自然語言處理
1. 數據處理
- 讀取數據
- 替換數字
輸出:(數字被替換了)
Turn to channel 1. Wechsle auf Kanal eins. Turn to channel _NUMBER_ . Wechsle auf Kanal eins.- 切分 輸入,輸出
- 輸入輸出句子的 最大長度
- 輸入輸出 tokens 個數
- 建立 tokens 與 id 的映射關系
2. 編碼器、解碼器數據
- 注意維度的意義
- 填充矩陣
2.1 編碼器
from keras.layers import Input, LSTM, Embedding, Dense from keras.models import Modelembedding_size = 256 # 嵌入維度 rnn_size = 64 # 編碼器 encoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None,)) encoder_after_embedding = Embedding(input_dim=num_encoder_tokens, # 單詞個數output_dim=embedding_size)(encoder_inputs) encoder_lstm = LSTM(units=rnn_size, return_state=True) # return_state: Boolean. Whether to return # the last state in addition to the output. _, state_h, state_c = encoder_lstm(encoder_after_embedding) encoder_states = [state_h, state_c] # 思想向量2.2 解碼器
# 解碼器 decoder_inputs = Input(shape=(None,)) decoder_after_embedding = Embedding(input_dim=num_decoder_tokens, # 單詞個數output_dim=embedding_size)(decoder_inputs) decoder_lstm = LSTM(units=rnn_size, return_sequences=True, return_state=True) decoder_outputs, _, _ = decoder_lstm(decoder_after_embedding,initial_state=encoder_states) # 使用 encoder 輸出的思想向量初始化 decoder 的 LSTM 的初始狀態 decoder_dense = Dense(num_decoder_tokens, activation='softmax') # 輸出詞個數,多分類 decoder_outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs)2.3 模型
model = Model([encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs], decoder_outputs) model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy']) model.summary()from keras.utils import plot_model plot_model(model,to_file='model.png')輸出:
Model: "model_1" __________________________________________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to ================================================================================================== input_1 (InputLayer) (None, None) 0 __________________________________________________________________________________________________ input_2 (InputLayer) (None, None) 0 __________________________________________________________________________________________________ embedding_1 (Embedding) (None, None, 256) 1465344 input_1[0][0] __________________________________________________________________________________________________ embedding_2 (Embedding) (None, None, 256) 2336256 input_2[0][0] __________________________________________________________________________________________________ lstm_1 (LSTM) [(None, 64), (None, 82176 embedding_1[0][0] __________________________________________________________________________________________________ lstm_2 (LSTM) [(None, None, 64), ( 82176 embedding_2[0][0] 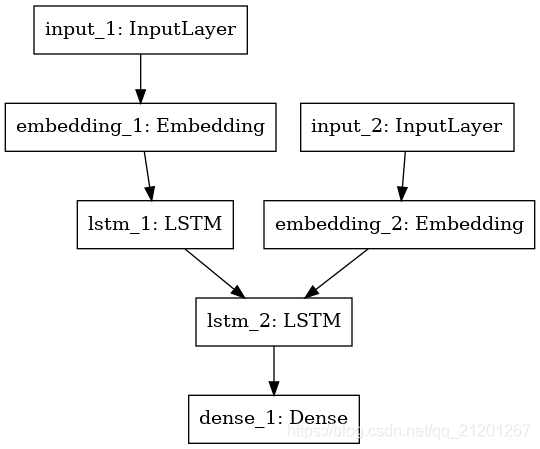lstm_1[0][1] lstm_1[0][2] __________________________________________________________________________________________________ dense_1 (Dense) (None, None, 9126) 593190 lstm_2[0][0] ================================================================================================== Total params: 4,559,142 Trainable params: 4,559,142 Non-trainable params: 0 __________________________________________________________________________________________________3. 訓練
- 訓練 + 回調函數保存最佳模型
- 繪制訓練曲線
4. 推理模型
- 編碼器
- 解碼器
初始狀態 + embedding 作為輸入,經過LSTM,輸出 decoder_outputs_inf, state_h_inf, state_c_inf
decoder_outputs_inf, state_h_inf, state_c_inf = decoder_lstm(decoder_after_embedding,initial_state=decoder_states_inputs) # 作為下一次推理的狀態輸入 h, c decoder_states_inf = [state_h_inf, state_c_inf] # LSTM的輸出,接 FC,預測下一個詞是什么 decoder_outputs_inf = decoder_dense(decoder_outputs_inf) decoder_model = Model([decoder_inputs] + decoder_states_inputs,[decoder_outputs_inf] + decoder_states_inf )5. 采樣
def decode_sequence(input_seq):# encoder_states = [state_h, state_c]states_value = encoder_model.predict(input_seq) # list 2個 array 1*rnn_sizetarget_seq = np.zeros((1, 1))# 目標輸入序列 初始為 'BEGIN_' 的 idxtarget_seq[0, 0] = outputToken_idx['BEGIN_']stop = Falsedecoded_sentence = ''while not stop:output_tokens, h, c = decoder_model.predict([target_seq] + states_value)# output_tokens [1*1*9126] h,c [1*rnn_size]sampled_token_idx = np.argmax(output_tokens)sampled_word = idx_outputToken[sampled_token_idx]decoded_sentence += ' ' + sampled_wordif sampled_word == '_END' or len(decoded_sentence) > 60:stop = Truetarget_seq = np.zeros((1, 1))target_seq[0, 0] = sampled_token_idx # 作為下一次預測,輸入# Update statesstates_value = [h, c] # 作為下一次的狀態輸入return decoded_sentence# 簡單測試 采樣 text_to_translate = 'Are you happy ?' encoder_input_to_translate = np.zeros((1, max_input_seq_len),dtype=np.float32) for t, word in enumerate(text_to_translate.split()):encoder_input_to_translate[0, t] = inputToken_idx[word]# encoder_input_to_translate [[ids,...,0,0,0,0]] print(decode_sequence(encoder_input_to_translate))輸出:
text_to_translate = 'Are you happy?' 輸出: Sind Sie glücklich? _END # 你高興嗎? text_to_translate = 'Where is my car?' 輸出: Wo ist mein Auto? _END # 我的車呢? text_to_translate = 'When I see you, I fall in love with you!' 輸出:Sind Sie mit uns gehen. _END # 你跟我們一起去嗎?注意:
- 待翻譯句子長度不能超過最大長度
- 且不能出現沒有出現過的詞匯,如 dear 出現過,但是與標點連著寫dear!沒有出現過,會報錯
總結
以上是生活随笔為你收集整理的使用LSTM建立seq2seq模型进行语言翻译的全部內容,希望文章能夠幫你解決所遇到的問題。

- 上一篇: LeetCode 1566. 重复至少
- 下一篇: 05.序列模型 W3.序列模型和注意力机
